产品基本信息
-
产品货号
BD-PA0195
-
别名
HIF1; MOP1; PASD8; bHLHe78; HIF-1alpha; HIF1-ALPHA; HIF1A
-
产品名称
HIF1A Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
-
类别
抗原抗体
-
基因名称
HIF1A
-
Clonality
Monoclonal
-
推荐应用
WB,IHC-P,ICC,Elisa
-
反应种属
Human,Mouse,Monkey
-
存储缓冲液
Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% New type preservative N.
-
Human Gene ID
3091
-
免疫原
Purified recombinant fragment of human HIF1A expressed in E. Coli.
-
稀释度
WB 1:500-1:2000, IHC-P 1:200-1:1000, ICC 1:200-1:1000, ELISA 1:10000
-
参考分子量
120kDa
-
运输及保存条件
4℃; -20℃ for long term storage. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
-
宿主
Mouse
-
同种型
IgG1
-
克隆号
1A3
图片
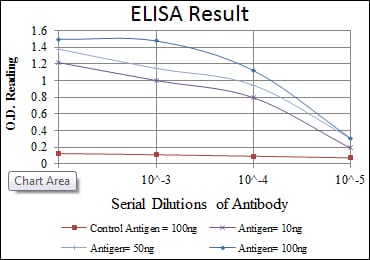 |
Red: Control Antigen (100ng); Purple: Antigen (10ng); Green: Antigen (50ng); Blue: Antigen (100ng); |
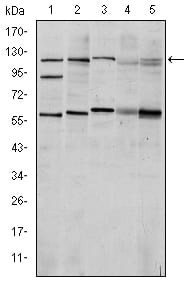 |
Western blot analysis using HIF1A mouse mAb against Cos7 (1), Hela (2), Jurkat (3), RAJI (4) and NIH/3T3 (5) cell lysate. |
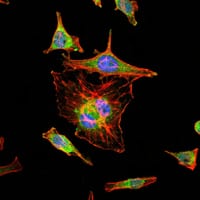 |
Immunofluorescence analysis of Hela cells using HIF1A mouse mAb (green). Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye. Red: Actin filaments have been labeled with Alexa Fluor-555 phalloidin. |
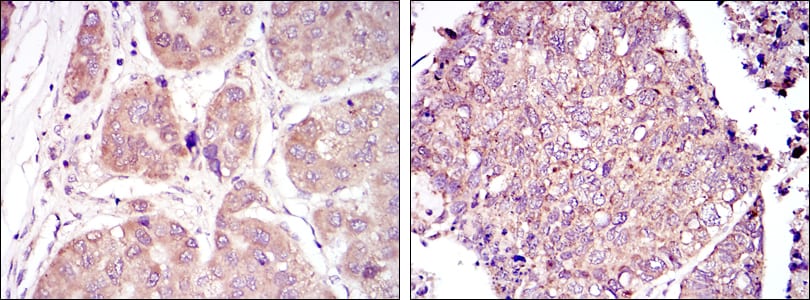 |
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer tissues (left) and lung cancer tissues (right) using HIF1A mouse mAb with DAB staining. |
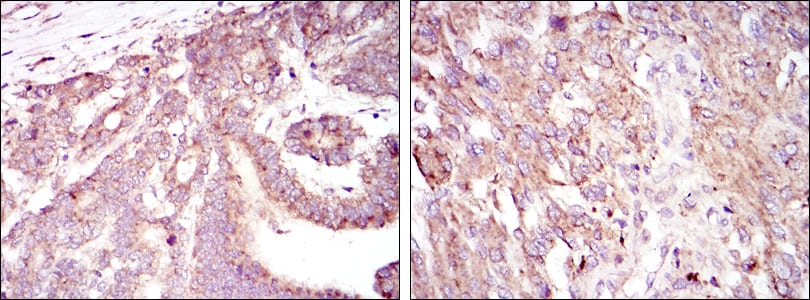 |
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human stomach cancer tissues (left) and brain tumor tissues (right) using HIF1A mouse mAb with DAB staining. |
产品详情
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF1) is a transcription factor found in mammalian cells cultured under reduced oxygen tension that plays an essential role in cellular and systemic homeostatic responses to hypoxia. HIF1 is a heterodimer composed of an alpha subunit and a beta subunit. The beta subunit has been identified as the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT). This gene encodes the alpha subunit of HIF-1. Overexpression of a natural antisense transcript (aHIF) of this gene has been shown to be associated with nonpapillary renal carcinomas. Two alternative transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified. (provided by RefSeq) Tissue specificity: Expressed in most tissues with highest levels in kidney and heart. Overexpressed in the majority of common human cancers and their metastases, due to the presence of intratumoral hypoxia and as a result of mutations in genes encoding oncoproteins and tumor suppressors.



 收藏
收藏





 电话咨询
电话咨询
 在线咨询
在线咨询
 QQ
QQ
 二维码
二维码
 扫码二维码
扫码二维码